OTR-AC (MK-2866 ESTER) SARM POWDER – 1000MG / 1 GRAM
$88.99
OTR-AC (MK-2866 Ester) SARM is sold for laboratory research use only. Terms of sale apply. Not for human consumption, nor medical, veterinary, or household uses. Please familiarize yourself with our Terms & Conditions prior to ordering.
*Includes:
- One (~10mg – 15mg) Red Micro Scoop
Also Available In:
![]() Liquid Option >>
Liquid Option >>
![]() Gel Option >>
Gel Option >>
- Description
- Additional information
Description
OTR-AC (aka MK-2866 Ester) SARM Powder
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

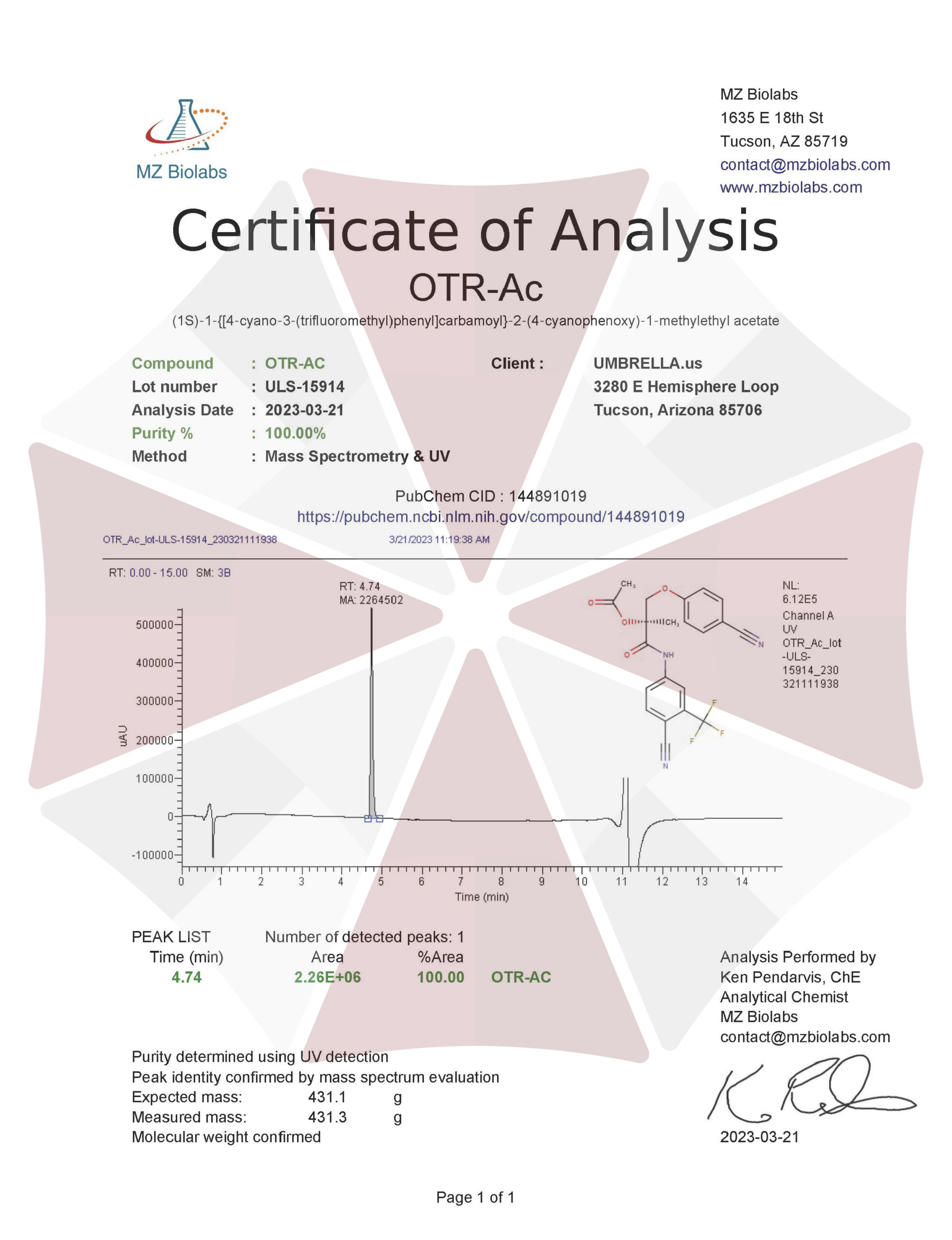
| CAS Number | 1025658-44-9 |
| Other Names | OTR-AC, Ostarinyl Acetate (MK2886 acetate), Ostarine acetate (MK2886 acetate), Ostarine acetate ester (MK2886 acetate ester), Ostarine acetic acid ester (MK2886 Acetic acid ester) |
| IUPAC Name | 5-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-1-[2-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]ethyl]indole-2-carboxylic acid |
| Molecular Formula | C₂₁H₁₆F₃N₃O₄ |
| Molecular Weight | 431.37 |
| Purity | ≥99% Pure (LC-MS) |
| Liquid Availability | |
| Powder Availability | |
| Gel Availability | |
| Storage | Store in cool dry environment, away from direct sunlight. |
| Terms | All products are for laboratory developmental research USE ONLY. Products are not for human consumption. |
*Includes:
- One (~10mg – 15mg) Red Micro Scoop

What is OTR-AC?
OTR-AC, also known as Ostarine-O-Acetate, is an esterified version of the popular selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM), MK-2866, or Ostarine. While the benefits elicited by the two compounds are extremely similar, the esterification process results in enhanced potency and effectiveness. SARMs are able to bind to androgen receptors, suggesting that they are able to mimic the actions of testosterone. Because SARMs do not elicit the typical negative side effects observed with testosterone treatment, these compounds are becoming more popular and widely available for research purposes.
Main Research Findings
1) The process of esterification leads to increased potency and improved efficacy of OTR-AC in comparison to its parent compound, MK-2866.
2) SARMs have been shown to promote various forms of functional therapy through tissue-selective activation of androgenic signaling.
3) Treatment with Ostarine in an ovariectomized rat model led to an improvement in muscle tissue in the test subjects.
Selected Data
1) As it was previously mentioned, OTR-AC is the esterified form of MK-2866. MK-2866, like most SARMs, is typically known for its ability to promote anabolic activity in bone and muscle tissue. Current research examines the potential of MK-2866 to enhance neuroprotection and stimulate antitumor activity. As an esterified version of MK-2866, OTR-AC has been shown to elicit similar effects as its parent compound with far more potency. The esterification process proceeds by combining an organic acid (RCOOH) and an alcohol (ROH) to form water and an ester (RCOOR) [1].
Furthermore, esterification reactions occur when a primary alcohol is treated with a carboxylic acid in the presence of sulphuric acid. The resulting compound tends to smell sweet and is generally classified as an ester compound. The chemical reaction typically takes place in 5 steps and follows the format:
CH3COOH + CH3CH2COOH → CH3COOCH2CH3
The first step of the esterification mechanism is cation formation. Step 2 of the mechanism delocalized the carbocation by protonating the carboxyl oxygen in order to improve the electrophilic properties of the carbocation. Step 3 transfers a proton to one of the hydroxyl groups to form a sufficient leaving group. Step 5 forms the pi bond by eliminating water and donating an electron pair from the hydroxyl group’s alcohol oxygen atom to the carbon atom. By eliminating water there is no feasible nucleophile available to reverse the reaction. This leads to step 5 which is the ultimate formation of an ester compound. These compounds typically have a pleasant smell, allowing them to be widely used in the perfume, food flavoring, and cosmetics industries. They are also organic compounds typically found in oils and fats that are able to be used and an organic solvent [1].
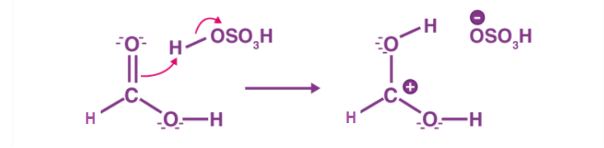
Figure 1: Step 1 of the esterification mechanism
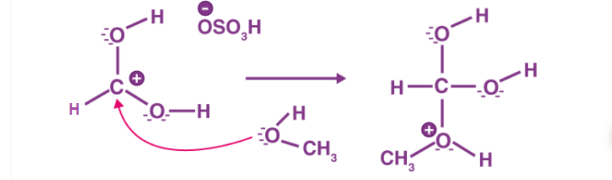
Figure 2: Step 2 of the esterification mechanism
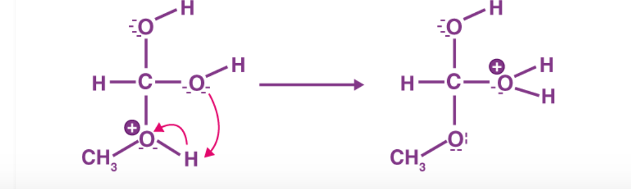
Figure 3: Step 3 of the esterification mechanism
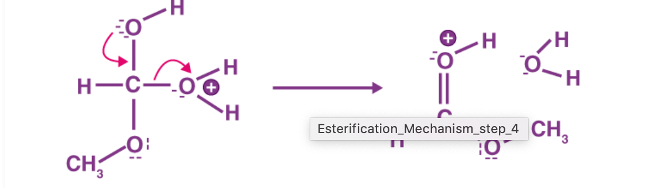
Figure 4: Step 4 of the esterification mechanism
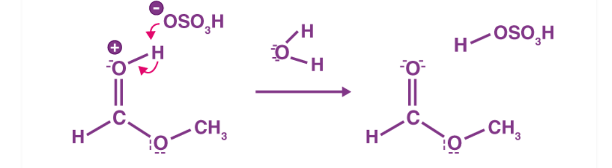
Figure 5: Step 5 of the esterification mechanism
2) The research team of Shalender Bhasin, MD and Ravi Jasuja, PhD. examined the potential of selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) to promote various forms of functional therapy. Previous research has reported that SARMs bind to androgen receptors and display tissue-selective activation of androgenic signaling, leading to anabolism in skeletal muscles and bones. The actions of SARMs are compared to testosterone, the major ligand for androgen receptors. Testosterone is often supplemented to men and women of all ages suffering from androgen deficiency and decreased muscle and bone wasting. However, administration of androgenic compounds such as testosterone is often related to many dose-limiting adverse side effects such as prostate dysfunction, edema, and erythrocytosis. On the other hand, SARM administration has been shown to result in similar anabolic activity without the adverse side effects associated with typical androgen treatment [2].
In order to target functional limitations caused by osteoporosis, aging, and chronic disorders, researchers first attempted to develop a SARM with the desired activity profile and tissue selectivity. The second approach included elucidating the mechanisms of action of androgens on skeletal muscles and the prostate in order to identify signaling molecules downstream of the androgen receptors that are capable of activating hypertrophic pathways in skeletal muscles but not the prostate. When observing the structure of SARMs, the compounds can be categorized into two groups: steroidal and nonsteroidal. Steroidal SARMs are synthesized by modifying the chemical structure of testosterone molecules. For example, substitution of 7-alpha alkyl makes testosterone less susceptible to 5-alpha reduction, thus increasing tissue selectivity with respect to the prostate. This results in the increased anabolic activity in the levator ani muscle and a decreased rate of anabolism in the prostate and seminal vesicles [2].
Researchers at the University of Tennessee and Ligand Pharmaceuticals reported early data regarding the discovery of nonsteroidal SARMs. After publication of the initial findings various other structural categories of SARM pharmacophores were examined. These categories included: aryl-propionamide, bicyclic hydantoin, quinolones, tetrahydroquinoline analogs, benzimidazole, imidazolopyrozole, indole, pyrazoline derivatives, azasteroidal derivatives, and aniline, diaryl aniline, and benzoxazepinones derivatives. The first generation of SARMS was developed by manipulating the structure of aryl propionamide analogs, bicalutamide and hydroxyflutamide. This initial discovery led to copious amounts of research dedicated solely to modifying compound structures in order to promote tissue selectivity and further hone in on the beneficial anabolic activity [2].
3) The first experiment conducted by the research team of Roch et. Al examined the effects of Ostarine treatment on muscle structure and metabolism. 3 month-old, female Sprague Dawley rats were ovariectomized (OVX) or left intact (non-OVX) and then randomly divided into five groups. Group 1: Non-OVX; Group 2: OVX; Groups 3 to 5: OVX rats treated with doses of Ostarine ranging from 0.04, 0.4, and 4 mg/kg (OVX + OS 0.04, OVX + OS 0.4, and OVX + OS 4). In order to properly investigate the dose-dependent effects of Ostarine both 10-fold and 100-fold dosages of the SARM were used; all SARM treatments took place over a period of 5 weeks [3].
The rats all received a soy-free rodent-based diet with Ostarine supplied with the meal. Food and demineralized water was provided ad libitum, while food intake and body weight were recorded by the research team, weekly. All food that remained in the cage was weighted weekly in order to calculate the average daily food intake of the rat by dividing the weight of the leftover food by the days between weighing the number of rats in one cage. The average daily dose of Ostarine was then calculated based on daily food intake and mean body weight. 13 weeks after OVX, the rats were euthanized and blood serum was collected in order to further analyze creatine kinase. Additionally, the uterus was weighed while the gastrocnemius muscle (GM), soleus muscle (SM), and the longissimus muscle (LM) were all extracted, weighted and stored in liquid nitrogen [3].
Muscle capillaries were stained using a modified PAS reaction followed by the application of a fixative solution to the serial cross-sections for 1 hour at 4 degree Celsius followed by 10 minutes at room temperature and extensive washing with distilled water. A-Amylase from porcine pancreas was added in 0.3% water solution and was used for 25 minutes for the hydrolyzation of polysaccharides followed by repeated washing with distilled water. The PAS reaction was performed next; 1% periodic acid was applied for 30 minutes followed by washing with distilled water and the application of Schiff’s reagent solution for 2-25 minutes under visual control to avoid overstaining. After the last step washing was performed by treating the samples with 10% potassium sulfite/1 N HCl/water (1:1:20) for 30 minutes, running tap water for 10 minutes, and distilled water for 3 minutes [3].
In terms of staining the muscle fibers, a fixative solution consisting of 1% paraformaldehyde solution, 1% CaCl2, and 6% sucrose applied to the fibers for 1 minute followed by washing with distilled water. This was followed by a modified staining technique utilizing adenosine-triphosphate (ATPase) The stained capillaries and fibers were digitally analyzed at 10-fold magnification while evaluation of the fibers was performed in three randomly chosen 1 mm^2 fields in the ATPase stained sections. Ninety slow-twitch oxidative (STO), fast-twitch oxidative (FTO), and fast-twitch glycolytic (FTG) fibers were skirted and since SM contains both STO and FTO fibers, only these fibers were measured and recorded. Evaluation of the stained capillaries was performed in two randomly chosen 0.25 mm^2 fields in the amylase-PAS stained sections. Capillary density was measured by the ratio of capillaries to fibers.
In order to identify and analyze activity of the primary muscle enzymes, lactate dehydrogenase, citrate synthase, and Complex I, samples were powdered and homogenized in Chappel-Perry medium. Muscle enzyme activity was measured via photometry while a BCA Protein Assay Kit and a multilabel reader were used to calculate protein content in the muscle fibers. Protein content was used to determine muscle enzyme activity. Additionally, intramuscular fat content was analyzed by boiling 5-10 grams of the homogenized quadriceps femoris muscle in hydrochloric acid for 1.5 hours in order to free occluded and bound lipid fractions. After filtration of the mass and drying the content of the filter was extracted and the fat content was defined as a percentage of the wet weight of the sample taken [3].
Discussion
1) As an esterified version of Ostarine, OTR-AC is considered a superior version of its parent compound due to its improved bioavailability and potency, as well as a 10-fold increase in half-life. The esterification process also makes OTR-AC far more stable than Ostarine suggesting that it is more effective and safe. While the benefits of the two compounds are very similar, there is debate regarding how much stronger OTR-AC is compared to Ostarine. Further research is required in order to know exactly how much more potent the esterified compound is in comparison to the parent compound.
Multiple research-based studies have concluded that SARMs are able to increase muscle mass and reduce fat, however, researchers thought it was important to note that OTR-AC does not reduce fat by targeting fat directly, but rather by raising metabolic rate. The compound increases testosterone leading to improved metabolism and increased energy expenditure, ultimately resulting in fat loss. Additionally, evidence suggests that OTR-AC is capable of increasing libido, improving recovery from exercise by increasing protein synthesis, and enhancing physical performance by boosting muscle mass and raising metabolism. Treatment with OTR-AC has also been linked to improved cardiovascular health as the esterified compound is capable of lowering levels of low-density lipoprotein [4].
2) The research team of Bhasin and Jasuja were able to achieve selectivity of SARMs by elucidating the mechanism of testosterone’s action on the prostate, as well as how molecules farther downstream were associated with activation of AR signaling in skeletal muscle. Analysis of muscle biopsies collected from male test subjects treated with varying doses of testestore revealed that administration of the compound led to hypertrophy in type I and type II muscle fibers. In relation to testosterone dosage, both type I and type II fibers experienced significant changes in cross-sectional areas. It is important to note that there was no change observed in the absolute number or the relative proportion of type I and type II fibers in response to testosterone administration [2].
Hypertrophy of the skeletal muscle was further examined through observation of muscle satellite cells and the myonuclear number. These variables were assessed through the use of electron microscopy, using direct counting and spatial orientation methods at baseline and after 20 weeks of GnRH agonist and testosterone enanthate treatment. Results reported that absolute and percent satellite cell number was significantly greater than baseline after 20 weeks of the test subjects receiving supraphysiologic doses of testosterone. The observed changes in the number of satellite cells correlated with changes in total and free testosterone levels, indicating that muscle fiber hypertrophy induced by testosterone is correlated with an increase in the number of satellite cells and the myonuclear number.
Recent studies have found that both testosterone and DHT are able to promote association between liganded ARs and beta-catenin, its co-activator. Beta-catenin is stabilized by this interaction and enhances translocation into the nucleus and association with TCF-4, as well as the transcriptional activation of Wnt-target genes. Additionally, Testosterone upregulated the expression of follistatin, resulting in increased muscle mass and decreased fat mass. SMAD 7 is also upregulated by testosterone while TGF-beta-mediated SMAD signaling in TGF-beta target genes is downregulated. The connection between testosterone and follistatin expression indicates that the effects of testosterone are cross-communicated from the WNT pathway to the TGF-beta-SMAD pathway. These results further suggest that candidate molecules located downstream of AR and beta-catenin, such as follistatin, have the potential to mediate the effects of testosterone on the muscle and may provide desired selectivity of anabolism. The discovery of these candidate targets allows for further research to be conducted in order to develop selective anabolic drugs [2].
3) Results of the study conducted by Roch et. Al reported that the average uptake of Ostarine calculated based on food intake and body weight was 0.03 ± 0.006 mg/kg/BW in the OVX+OS 0.04 group, 0.3 ± 0.07 mg/kg/BW in the OVX+OS 0.4 group, and 3.0 ± 0.83 mg/kg/BW in the OVX+OS 4 group. The average food intake was found to be 22.3 ± 4.6 g/rat/day in all groups, however rats in the non-OVX groups consumed less food during weeks 2 to 5 in comparison to the rats in all other groups. Additionally, the measured body weight of the rats across all treatment groups were similar at the beginning of the study. Ovariectomy led to a significant increase in body weight in all four OVX groups compared to the non-OVX group. Ostarine treatment did not have any significant influence on body weight [3].
The researchers found that the uterine weight in all four OVX groups was significantly lower in comparison to the non-OVX groups. The OVX subjects treated with 0.04 mg of Ostarine did not experience any significant changes in uterine weight in comparison to the OVX control group. However, uterine weight increased in the OVX subjects treated with 0.4 and 4 mg/kg of Ostarine. Ostarine treatment was also found to have resulted in a dramatic increase in GM weight while the weight or 5he SM did not differ significantly between experimental groups.
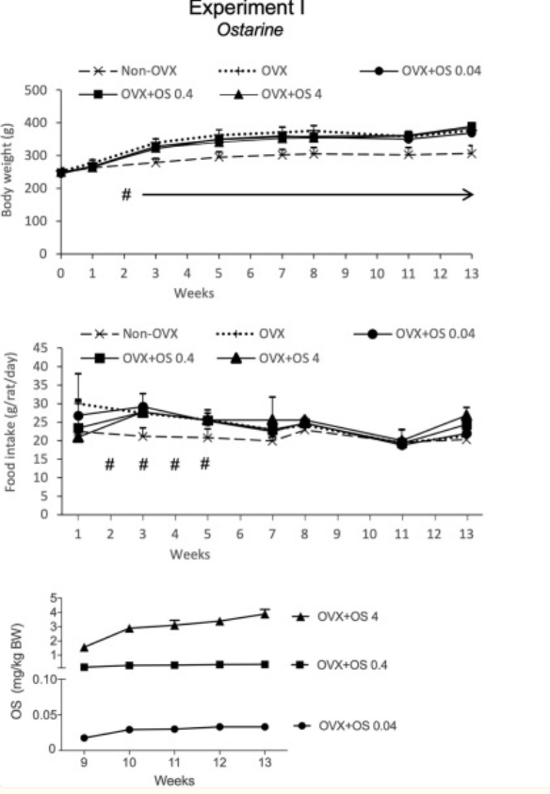
Figure 6: Changes in body weight, daily food intake, and Ostarine intake over the experimental period
In terms of muscle vascularization, treatment with Ostarine resulted in higher capillary density in GM and LM. In comparison to the OVX control group, treatment with 0.04 and 4 mg/kg resulted in a significantly higher capillary density. Treatment with 0.4 and 4 mg/kg of Ostarine resulted in increased capillary density in the LM in comparison to both the non-OVX and OVX groups. Ostarine treatment did not affect the number of capillaries in the SM. When observing changes in the muscle fiber size and distribution there were no significant changes in the diameter of STO, FTO, and FTG fibers of the GM, LM and SM elicited by Ostarine treatment. This result was independent of the dosage of Ostarine administered to the subjects. There were also no observed differences in muscle fiber distribution in the LM [3].
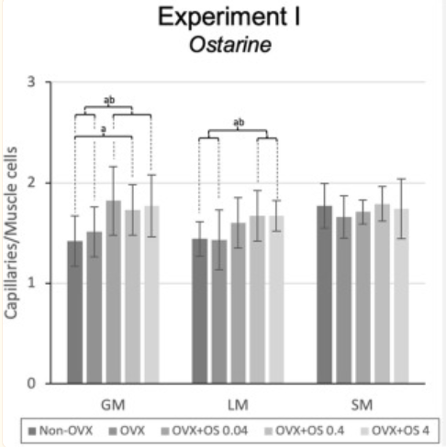
Figure 7: changes in muscle cells/capillary density in response to treatment with varying doses of Ostarine.
When evaluating enzyme activity in the muscles in response to Ostarine treatment, the researchers found that citrate synthase activity in the LM was significantly higher in the OVX + OS 4 treatment group in comparison to the non-OVX control group. These results were not seen in the SM and GM. Additionally, the activity of LDH and Complex I did not not change among the groups in all three muscle groups studied. Similarly, after the subjects were ovariectomized there were no changes in serum creatine kinase levels after treatment with Ostarine [3].
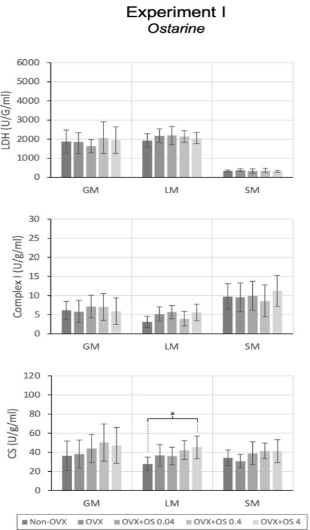
Figure 8: changes in enzyme activity in response to treatment with varying doses of Ostarine.
Disclaimer
**LAB USE ONLY**
*This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. THE PRODUCTS DESCRIBED HEREIN ARE FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. All clinical research must be conducted with oversight from the appropriate Institutional Review Board (IRB). All preclinical research must be conducted with oversight from the appropriate Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) following the guidelines of the Animal Welfare Act (AWA).
Citations
[1] “Esterification (Alcohol & Carboxylic acid) – Reactions Mechanism & Uses with Videos.” Byju’s, https://byjus.com/chemistry/esterification/. Accessed 6 June 2023.
[2] Bhasin S, Jasuja R. Selective androgen receptor modulators as function promoting therapies. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2009 May;12(3):232-40. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e32832a3d79. PMID: 19357508; PMCID: PMC2907129.
[3] Roch PJ, Henkies D, Carstens JC, Krischek C, Lehmann W, Komrakova M, Sehmisch S. Ostarine and Ligandrol Improve Muscle Tissue in an Ovariectomized Rat Model. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Sep 17;11:556581. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.556581. PMID: 33042018; PMCID: PMC7528560.
[4] Narayanan R, Mohler ML, Bohl CE, Miller DD, Dalton JT. Selective androgen receptor modulators in preclinical and clinical development. Nucl Recept Signal. 2008;6:e010. doi: 10.1621/nrs.06010. Epub 2008 Nov 26. PMID: 19079612; PMCID: PMC2602589.
OTR-AC (MK-2866 Ester) SARM is sold for laboratory research use only. Terms of sale apply. Not for human consumption, nor medical, veterinary, or household uses. Please familiarize yourself with our Terms & Conditions prior to ordering.




| File Name | View/Download |
| 03-21-2023-Umbrella-Labs-OTR-Ac-Certificate-Of-Analysis-COA.pdf |
VIEW CERTIFICATES OF ANALYSIS (COA)
Additional information
| Weight | 2 oz |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 3 × 3 × 5 in |




















